Sheep Brain Dissection: A Comprehensive Guide
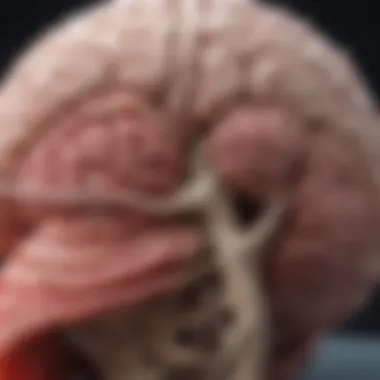

Intro
Sheep brain dissection is a key aspect of biological studies, particularly in understanding mammalian neuroanatomy. This practical approach not only provides students and professionals with hands-on experience but also allows for observations of intricate brain structures. The sheep brain is often chosen due to its size and anatomical similarities to the human brain, making it a valuable resource for educational purposes. This guide seeks to illuminate various facets of sheep brain dissection, providing insights into its importance in both research and education.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Dissecting a sheep brain reveals multiple essential anatomical features. Key findings often highlight the complexity of structures such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Each area plays a critical role in neurological functions ranging from movement to processing sensory information. Research indicates that performing dissections allows for better retention of anatomical knowledge compared to traditional textbook learning. Furthermore, studies suggest that engaging with physical specimens enhances skills in observational precision and critical thinking.
Relevance to Current Scientific Discussions
In contemporary science, understanding brain anatomy is paramount in fields such as psychology, neurology, and medical education. Dissection provides a tactile learning experience that complements theoretical knowledge. Current discussions emphasize a move towards experiential learning in biology. The ethical considerations surrounding the use of animal specimens are also increasingly prominent, leading to debates on best practices and humane conduct in educational settings. These discussions highlight the need for a balance between effective learning outcomes and ethical responsibility.
Methodology
Research Design and Approach
The approach to study sheep brain dissection combines both qualitative and quantitative methods. Students typically undergo instructional sessions before performing dissections. This dual approach ensures that learners build a theoretical foundation and enhance their practical skills. The lessons encompass anatomy lectures, demonstrations of dissection techniques, and hands-on laboratory practice.
Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
Data collection during dissections involves documentation of observations, photographic evidence, and sometimes video recordings. Students may utilize checklists to ensure all anatomical features are noted. Post-dissection, analysis often includes comparative discussions on anatomical variations across species. This practice reinforces learning, encouraging students to synthesize information and reflect on dissection outcomes.
"Learning through direct engagement with biological specimens fosters deeper understanding and retention of complex concepts."
In summary, sheep brain dissection serves as a foundational tool in biological education, bridging theory with practice. The significance of this activity extends beyond the classroom, influencing current research and ethical discussions in science.
Foreword to Sheep Brain Dissection
Sheep brain dissection serves as a cornerstone for understanding neuroanatomy and is a fundamental component of biological education. This practice enables students and professionals to explore the intricacies of brain structure firsthand. By engaging in this meticulous dissection process, one can develop a deeper appreciation for the complexities inherent in the anatomy of the brain.
In many academic settings, this procedure is introduced early in the curriculum, as it provides practical insights that are complementary to theoretical learning. Dissection allows for the visual and tactile exploration of various brain regions and their functions. As students handle real specimens, they gain valuable experience that enhances the learning of abstract concepts found in textbooks.
Historical Context
The practice of dissection has long been utilized in medicine and biology. Historically, the dissection of animal brains, particularly those of sheep, has contributed significantly to our understanding of the nervous system. The choice of sheep as a specimen is partly due to their physiological similarities to humans. Ancient scholars and anatomists such as Galen and Vesalius laid the groundwork for modern anatomical studies, emphasizing the importance of direct observation and hands-on experience in understanding biological structures.
In recent decades, the use of sheep brains in educational settings has become standardized. This change was influenced by advances in ethical considerations and educational policies that aim to provide students with a realistic approach to anatomy without resorting to the use of human specimens. Thus, sheep brain dissection has a rich heritage in contributing to scientific knowledge and education.
Importance in Biological Studies
The significance of sheep brain dissection extends beyond mere anatomy; it plays a vital role in neurological research and educational dynamics. For students of biology and neuroscience, this practical experience is invaluable. Dissecting a sheep brain allows students to correlate theoretical knowledge with real-life biological processes.
Understanding the anatomy of the brain through dissection paves the way for further exploration in various related disciplines such as psychology, medicine, and veterinary studies. Not only does this activity fulfill educational requirements, but it also fosters critical thinking skills as students analyze the physiological functions of different brain regions.
Furthermore, the applications of insights gained from sheep brain studies are profound. Research derived from such dissections has implications in developing treatments for neurological diseases and enhancing educational tools for future learning. Overall, the role of sheep brain dissection in biological studies cannot be understated, as it embodies the integration of theory and practice in the scientific process.
Anatomy of the Sheep Brain
Understanding the anatomy of the sheep brain is crucial for anyone involved in biological studies or dissections. The sheep brain serves as a valuable model due to its similarities with the human brain, allowing researchers to draw significant parallels. This anatomical knowledge enhances dissection skills and informs individuals about brain functions and their relevance to various studies, such as neurology, veterinary science, and education.
External Structures
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the sheep brain and is responsible for higher brain functions such as thought and action. Its structure is divided into two hemispheres, which contribute to its complexity. The key characteristic of the cerebrum is its role in processing sensory information and coordinating voluntary movements. This makes it a popular choice for study in both educational settings and research.
One unique feature of the cerebrum is the presence of folds, known as gyri, and grooves, called sulci. These structures increase the surface area available for neurons, enhancing cognitive capabilities. The cerebrum also holds importance in understanding neurological diseases, as many of these conditions affect higher cognitive functions.
Cerebellum


The cerebellum, the second largest part of the brain, is located under the cerebrum. It primarily coordinates voluntary movements and is crucial for balance and posture. The key characteristic of the cerebellum is its intricate structure, which includes layers of neurons that continually process information.
Its unique feature lies in its ability to fine-tune movements by receiving input from other brain parts and sensory systems. This is particularly advantageous in studies of motor control. The cerebellum's contribution to understanding movement disorders makes it significant in both educational contexts and practical research applications.
Brainstem
The brainstem connects the brain with the spinal cord and is essential for maintaining basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and wakefulness. The key characteristic of the brainstem is its role as a relay center for information traveling between the brain and the body.
The unique feature of the brainstem is its division into three parts: the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Each part has specific functions that are vital for survival. Understanding the brainstem is beneficial in neuroanatomy and can help students grasp the essential functions that support life, making it a focus in both dissections and neurological studies.
Internal Features
Ventricles
The ventricular system of the sheep brain comprises fluid-filled spaces that provide cushioning and support. Ventricles help circulate cerebrospinal fluid, which nourishes the brain and removes waste. The key characteristic of the ventricles is their role in maintaining homeostasis within the brain.
A unique feature is the lateral ventricles, which are the largest. They are critical in research related to brain injuries and diseases like hydrocephalus. This understanding is useful for students and researchers looking to explore the fluid dynamics that affect brain health.
Gray and White Matter
Gray and white matter are two distinct tissue types within the brain, each with specific functions. Gray matter contains neuron cell bodies and is primarily involved in processing information, while white matter consists of myelinated axons that transmit signals between different regions. The key characteristic of gray matter is its role in neural processing, whereas white matter is crucial for communication between brain regions.
A unique feature of the gray matter is its location on the brain's surface, while white matter is found deeper inside. Understanding these components is paramount in fields such as neurology and psychology, making them a crucial aspect of sheep brain dissections and educational programs.
Preparation for Dissection
Preparation is an essential part of sheep brain dissection. The right tools and safety protocols set the foundation for a successful and informative dissection experience. Proper preparation ensures that dissection can be conducted smoothly, enabling students and researchers to focus on learning and comprehending the structures and functions of the brain without interruptions or complications.
Tools and Equipment
Understanding the tools and equipment needed for dissection is crucial. Each instrument has unique characteristics that enhance the dissection process.
Scalpels
A scalpel is crucial for making precise incisions. Scalpels identified by their fine, sharp blades allow for accurate cuts. This quality is significant because accuracy affects the ability to identify different brain structures visually.
They are typically popular due to their effectiveness in making clean cuts. One advantage is their replaceable blades, ensuring consistent sharpness, while the downside is the need for careful handling to avoid injuries.
Forceps
Forceps play an important role in handling tissues during the dissection. They are designed for grip and control, making them ideal for holding delicate brain structures. Their key characteristic of having varying degrees of jaw strength allows for both gentle and firm handling. This flexibility makes forceps a beneficial choice in dissection, as they can assist in both removing membranes and repositioning structures for better visibility. However, they require practice to master their use effectively, especially in delicate tasks.
Dissection Pan
A dissection pan is where all the action happens. It provides a stable surface for laying out the sheep brain during dissection, which is crucial for organization and ease of access. The benefit of having a specific dissection pan is the raised edges that contain fluids, allowing for a cleaner workspace. This minimizes clutter, which is particularly useful when handling multiple structures at once. While standardized pans are available, non-slip options may offer added stability during procedures.
Safety Protocols
Safety measures are not merely recommendations; they are necessary for conducting dissection safely and responsibly. They protect individuals involved and promote ethical standards in the scientific community.
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is indispensable. Wearing gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles protects individuals from biological hazards. Comfort is also a key aspect since it enables individuals to focus on dissection without distractions. PPE acts as a barrier, reducing direct contact with biological materials that could be harmful. Ensure that PPE is fitted properly; a poor fit may not offer adequate protection.
Hygiene Practices
Hygiene practices are vital in maintaining a clean workspace. Regular cleaning of tools and surfaces minimizes contamination risk. The main aspect of hygiene includes washing hands thoroughly before and after handling any biological material. Disinfecting all tools before use prevents cross-contamination and upholds health standards. Following strict hygiene practices contributes positively to both effective dissection and overall research credibility.
"Proper preparation reflects professionalism and commitment to ethical research practices."
In summary, preparation for sheep brain dissection involves both the selection of appropriate tools and strict adherence to safety protocols. Understanding the specifics of tools like scalpels, forceps, and dissection pans enhances the dissection process. At the same time, implementing robust safety measures ensures a secure and ethical environment for exploration and educational growth.
Dissection Techniques
Understanding dissection techniques is vital for anyone engaging in sheep brain dissection. These methods not only ensure effective identification of anatomical structures but also contribute to the overall educational experience. A well-executed dissection can enhance the learning outcome, providing practical insights alongside theoretical knowledge. The techniques described in this section are designed to promote accuracy and precision, making them essential for students, educators, and professionals alike.
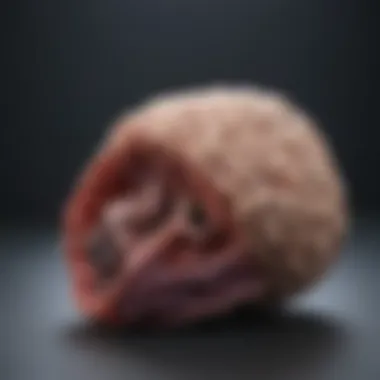

Step-by-Step Guide
Incision Techniques
Incision techniques are foundational in the dissection process. These methods involve making precise cuts to explore the brain layers systematically. The key characteristic of incision techniques is their ability to minimize damage to surrounding tissues while allowing for clear visibility of structures. A popular choice among educators and students, these techniques contribute significantly to the understanding of the brain's anatomy.
One unique feature of incision techniques is the various approaches that can be utilized based on specific objectives. For example, the transverse incision allows for thorough observation of brainstem structures, while an anterior-posterior approach can help reveal the cerebrum effectively. Each method has its own advantages, such as improving clarity during observation, and disadvantages, like increased risk of cutting delicate areas if performed by inexperienced individuals.
Identifying Structures
Identifying structures within the sheep brain is a crucial skill developed during dissection. The key characteristic of this process is the focus on recognizing and differentiating significant brain components accurately. This skill is essential as it supports deeper comprehension of brain functions and pathways, which are critical for education and research.
A unique feature of identifying structures is the use of anatomical landmarks that guide the dissection. These landmarks provide a reference point for students to assess the organization of the brain. While this technique is beneficial in enhancing anatomical understanding, it can pose challenges. For instance, the intricate nature of neural networks sometimes results in misidentification if not approached with care.
Common Challenges
Despite its educational value, several challenges arise during the dissection process. Recognizing these challenges is important for a successful dissection experience.
Tissue Preservation
Tissue preservation is critical in maintaining the integrity of the brain during dissection. The key characteristic of this aspect is its focus on using appropriate techniques and solutions to minimize degradation. Proper preservation methods allow for quality observation of brain structures, enhancing the learning experience.
A significant aspect of tissue preservation is the use of formalin or glycerin solutions. These chemical agents effectively slow down decomposition. However, they also present a challenge. For example, excessive exposure can make certain structures appear opaque, thus reducing visibility. Hence, a balance must be maintained between adequate preservation and optimal visibility.
Navigating Complex Structures
Navigating complex structures is another challenge faced during dissection. The sheep brain comprises various interconnected systems, which can be daunting for newcomers. The key characteristic of this navigation is the intricate layout of the brain, where many components have close associations with one another.
An advantage of being mindful of this complexity is the enhancement of spatial awareness. As students practice navigating these structures, they develop critical observational skills. However, this can also lead to confusion, especially if one lacks familiarity with the anatomy. Overall, diligent practice and attentiveness can mitigate these difficulties, ultimately enriching the educational journey.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are vital when it comes to sheep brain dissection. Understanding the ethical implications ensures that researchers and educators are responsible in their approach. This section delves into two critical aspects: animal welfare and the associated regulations and guidelines.
Animal Welfare
Animal welfare is a significant concern in any scientific procedure involving animals. It reflects on how animals are treated, and it is essential to foster humane practices throughout the process of dissection.
- Respect for Animals: Dissection should only be performed under conditions that respect the life of the animal. It is crucial to use animals that have been euthanized humanely, ensuring no unnecessary suffering occurs.
- Purpose and Justification: The decision to utilize a sheep brain for dissection must be justified by the educational or scientific benefits. Researchers should consider whether the insights gained outweigh the ethical implications of using an animal.
- Training for Students: Students engaged in dissections should receive proper training. Understanding the significance of their work helps promote a sense of responsibility and respect for life.
"Raising awareness about these ethical aspects is imperative for fostering a responsible scientific community."
Regulations and Guidelines
Regulations and guidelines provide a framework for conducting ethical dissections. They serve to protect the welfare of the animals involved and ensure responsible education and research practices.
- Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC): Many institutions have IACUCs that oversee animal research activities. These committees ensure that all procedures involving animals align with ethical standards and provide oversight to minimize harm.
- Legal Frameworks: Various laws regulate the treatment of animals in research. In the United States, for instance, the Animal Welfare Act governs the handling and care of animals used in research and education. Adhering to such regulations is non-negotiable.
- Ethical Guidelines and Training: Many educational institutions provide ethical guidelines and training for students and researchers. This education emphasizes the responsibility of each individual involved in dissection to uphold humane treatment and make informed decisions regarding the use of animal specimens.
Applications of Sheep Brain Research
The exploration of sheep brain research plays a crucial role not only in advancing scientific knowledge but also in practical applications across various disciplines. This section delves into the intricate relationship between sheep brain studies and their contributions to numerous fields, specifically focusing on neurological studies and educational utility. Each application highlights the importance of dissecting and analyzing the sheep brain as a model for understanding complex biological functions.
Neurological Studies
Sheep brains serve as an important model for neurological studies. These brains share many anatomical and functional similarities with human brains, making them valuable for researchers. The insights gained from sheep brain dissections can help uncover mechanisms underlying neurological disorders and diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- One significant area is the study of neurodegenerative conditions. Research involving sheep brains can simulate effects observed in human patients. This can lead to improved understanding of disease progression and potential therapeutic avenues.
- Additionally, sheep brain tissues are often used in experiments investigating synaptic connections and plasticity, key components of learning and memory. The ability to study these processes contributes to advances in cognitive neuroscience.
Utilizing sheep brains allows researchers to conduct ethically sound experiments, as they are sourced in compliance with animal welfare regulations. Furthermore, this research has broader implications. It informs clinical practices and enhances the development of treatment strategies.
Educational Utility


The educational benefits of studying sheep brains are profound. Dissection programs using sheep brains engage students at various levels, from high school to graduate studies.
- Hands-On Learning: Students gain practical experience in anatomy and physiology, directly observing brain structures and functions. This type of active learning is effective at cementing theoretical knowledge in a tangible manner.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: The integration of sheep brain dissection into biological curricula enhances understanding of complex systems, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Students are often tasked with identifying anatomical features, which requires careful observation and analytical reasoning.
- Research Skills Development: Dissection experiences cultivate essential laboratory skills, such as precision and attention to detail. These skills are transferable and beneficial for future scientific endeavors.
Educational exposure to sheep brain research enriches the academic experience, providing students with tools necessary for careers in medicine, research, and education.
In summary, the applications of sheep brain research extend far beyond the lab. Through neurological studies, researchers gain insights that can lead to medical breakthroughs. Simultaneously, educational initiatives foster a new generation of scientists equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary for future challenges.
Educational Benefits of Dissection
Dissection of the sheep brain offers valuable educational benefits for students and researchers alike. It is not merely a practical exercise; it transforms theoretical knowledge into tangible experiences which enhances learning in various disciplines including biology, neurology, and even psychology. Understanding biological functions through dissection fosters an environment where academic concepts can be applied to real-world situations, improving retention and comprehension.
Enhancing Understanding of Anatomy
Exploring the anatomical features of the sheep brain enables students to visualize structures that are often only seen in textbooks. The act of dissecting provides insights into the complex relationships between different parts of the brain. For instance, a student can understand the functions of various lobes like the occipital lobe associated with vision and the temporal lobe related to auditory processing.
Key benefits include:
- Tactile Learning: Hands-on experience makes anatomy lessons memorable.
- Visualization of Theory: Connecting physical structures with their functions enriches theoretical knowledge.
- Fostering Curiosity: The dissection process encourages questions and deepens interest in biology.
Students also learn about differences in brain structure across species. This knowledge can lead to a better appreciation of evolutionary biology and comparative anatomy.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Dissection challenges students to think critically about the materials at hand. They must analyze the relationships between anatomy and function. During the dissection, students encounter unexpected conditions, requiring them to adapt their strategies or methods accordingly. Such experiences are crucial for developing problem-solving skills.
The critical thinking process during dissection includes:
- Observation: Noticing details that are sometimes overlooked in diagrams.
- Hypothesis Formulation: Making educated guesses about the function of different structures based on their appearance.
- Decisional Making: Choosing the best dissection techniques or tools based on the specific needs of the tissue.
As students navigate complexities of anatomy and function, they gain a deeper appreciation for scientific inquiry, preparing them for careers in health sciences, research, and beyond.
"Hands-on experience with sheep brain dissection cultivates a rich learning environment, bridging the gap between theory and practice."
Through these educational benefits, engaging with the sheep brain directly contributes to a more robust understanding of both anatomical studies and the critical thinking demanded in scientific exploration.
End
The conclusion of this article serves several important purposes, drawing together the intricate threads discussed throughout. Understanding sheep brain dissection is not just about the practical skills involved but also encompasses a broader appreciation of the biological sciences. Learners gain insights into both anatomy and physiology by engaging with the physical structures of the brain. This fundamental knowledge lays a foundation for further exploration in fields such as neuroscience and medicine.
Summarizing Key Insights
Throughout this guide, we examined the anatomy of the sheep brain, highlighting significant structures like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The dissection process itself was detailed, introducing precise techniques and addressing common challenges. Ethical considerations were also underscored—reflecting the need for humane practices and adherence to regulations. These elements culminate in enhancing educational experiences, fostering critical thinking, and enabling practical applications in biological research. The intersection between theory and practice becomes a vital aspect of education in biological sciences.
Future Implications for Research and Education
The implications of sheep brain dissection extend beyond mere academic interest. As techniques become more refined and ethical standards evolve, the potential for advancing neurological research increases significantly. Future studies may incorporate technological advancements like imaging techniques or simulation models.
In educational contexts, the skills honed through dissection can prepare students for various careers in health and biological fields. Promoting hands-on learning experiences will enable learners to develop not only anatomical knowledge but also a nuanced understanding of the complexities of brain function. These developments signal a promising future for both educational frameworks and scientific discovery, reinforcing the importance of dissection in understanding neuroanatomy and its profound relevance in both research and applied sciences.
Academic Journals
Academic journals provide a repository of peer-reviewed research that is vital for any scientific inquiry. They represent the forefront of research and discovery in anatomical studies and dissection techniques. For those engaging in sheep brain dissection, articles published in reputable journals can offer insights into recent findings, methodologies, and best practices derived from expert analyses.
Some notable academic journals that frequently publish relevant research include:
- The Journal of Neuroscience
- Anatomical Record
- Brain Research
These journals often feature studies that discuss the practical applications of sheep brain research in neurology, behavior, and physiology. Accessing articles from these sources not only enriches the understanding of the subject matter but also equips readers with the latest information necessary for conducting thorough dissections and analyses themselves.
Educational Resources
Educational resources are integral for those looking to understand and apply the techniques surrounding sheep brain dissection. These resources take various forms, from textbooks to online platforms that specialize in anatomy education. They offer structured information and visual guides, which can enhance learning and execution of dissection procedures.
Some valuable resources include:
- Gray's Anatomy for Students – a comprehensive textbook that covers anatomical structures in detail.
- Websites like Khan Academy and Coursera, where courses on anatomy and dissection can be found.
- Various YouTube channels that demonstrate dissection techniques, providing visual aids that complement theoretical knowledge.
Utilizing these resources helps learners grasp complex concepts more effectively and develop the hands-on skills needed for successful dissection. By integrating academic research with educational tools, readers can create a well-rounded, informed approach to sheep brain dissection.



