Lymph Nodes with Fatty Hilum in Breast: An In-Depth Analysis


Intro
Lymph nodes with fatty hilum in the breast have gained notable attention in both clinical and academic discussions. These structures play a crucial role in the body's lymphatic system, serving as filtration points for the lymphatic fluid. This article aims to dissect the significance of these lymph nodes, especially in the context of breast health. Understanding the anatomy and physiological roles of lymph nodes with a fatty hilum is vital for diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Research indicates that the presence of fatty hilum in lymph nodes can be an important factor in distinguishing benign from malignant conditions. Fatty hilum generally correlates with non-tumorous lymph nodes that have not been compromised by the spread of cancer. Several studies have also highlighted that imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and MRI, can effectively evaluate these lymph nodes. Their histological features also provide insights into tissue health and can delineate different pathological states.
Relevance to Current Scientific Discussions
The significance of lymph nodes with a fatty hilum is becoming more relevant in oncological discussions. In recent years, healthcare professionals are emphasizing their importance in evaluating lymphatic involvement in breast cancers. The differentiation of benign versus malignant processes via histology and imaging can aid in establishing robust treatment plans and monitoring disease progression.
Methodology
Research Design and Approach
The examination of lymph nodes with fatty hilum involved a multi-faceted research approach. Studies typically employed both retrospective and prospective designs to gather extensive data. Clinical cases were analyzed along with existing literature to find common trends and anomalies in the presence of fatty hilum.
Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
Data was collected using various techniques, including clinical assessments, imaging, and histological examinations. Quantitative imaging methods were often used in conjunction with qualitative histological analysis. This combined methodology has enriched the understanding of lymphatic health within breast tissue, leading to more precise clinical applications.
"The role of lymph nodes in breast health cannot be overstated; understanding their characteristics is key to effective diagnosis."
In summary, lymph nodes with fatty hilum in the breast serve as critical indicators in the healthcare landscape. The anatomical and physiological insights derived from these lymph nodes are invaluable for ongoing research and clinical practice.
Prelude to Lymph Nodes in the Breast
The lymphatic system plays an essential role in the body's immune response and fluid balance. Understanding lymph nodes, especially those located in the breast, is crucial for both diagnostic and therapeutic contexts. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of lymph nodes with fatty hilum in breast tissue. These specific nodes are often indicators of various conditions and contribute significantly to how healthcare professionals assess breast health.
By examining their anatomical structure, imaging techniques, and clinical implications, this exploration will offer valuable insights not only for researchers and healthcare professionals but also for students pursuing knowledge in breast anatomy and pathology. Special attention is paid to how the presence of a fatty hilum can influence the differentiation between benign and malignant conditions.
Overview of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is an intricate network that includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells. This system is pivotal in transporting lymph, which is necessary for maintaining fluid balance in tissues and facilitating immune responses. The lymphatic vessels drain excess interstitial fluid from the tissues, which then passes through the lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes serve as filtration points, allowing for the identification and potential destruction of pathogens, cancer cells, and cellular debris. This filtering process is critical during immune responses, as activated lymphocytes within the nodes respond to foreign invaders or abnormal cells. The health and function of lymph nodes are vital indicators of the overall condition of the lymphatic system and, by extension, the entire immune system.
Role of Lymph Nodes in Breast Tissue
Lymph nodes in the breast region play a dual role. Firstly, they are essential in the immune response to infections or malignancies in breast tissue. Secondly, they serve as pathways for cancer metastasis. When breast cancer occurs, cancerous cells can invade lymphatic vessels and settle in nearby lymph nodes.
The presence of fatty hilum in lymph nodes is often considered a normal finding. Fatty hilum refers to the fatty area present at the center of some lymph nodes on imaging studies. This fat can indicate a node's physiological state, suggesting reactivity or benign processes.
Regular assessment of breast lymph nodes through imaging techniques offers insights for diagnosing conditions and determining treatment plans. Comparing normal lymph nodes with those exhibiting malignant characteristics can guide clinicians in making effective decisions regarding patient management.
"The lymphatic system serves as a critical interface between the immune system and the circulatory system, mediating responses that are vital for maintaining health."
Understanding the role and anatomy of lymph nodes in the breast, particularly with the presence of a fatty hilum, is important for accurate cancer assessments and developing future treatment approaches.
Anatomical Structure of Lymph Nodes
The anatomical structure of lymph nodes is integral to understanding their function and significance in the breast's lymphatic system. Lymph nodes serve multiple purposes, including filtering lymph fluid, housing immune cells, and facilitating the body’s immune response. The structure of these lymph nodes, including their morphology, components, and especially the fatty hilum, provides key insights into their operational role.
Basic Morphology of Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes exhibit a distinct morphology that aids in their function. Each lymph node is typically oval or bean-shaped and ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters in size. They are encapsulated by a fibrous capsule that gives structural support. The interior of the lymph node is divided into two major regions: the cortex and the medulla.
- Cortex: The outer region, which contains numerous follicles. These follicles predominantly host B lymphocytes, a type of immune cell crucial for the production of antibodies.
- Medulla: The inner region, which contains medullary cords and sinuses, predominantly occupied by T lymphocytes and plasma cells.
This unique structure allows lymph nodes to serve as efficient filtering stations for lymphatic fluid, trapping pathogens and cellular debris.
Understanding the Fatty Hilum
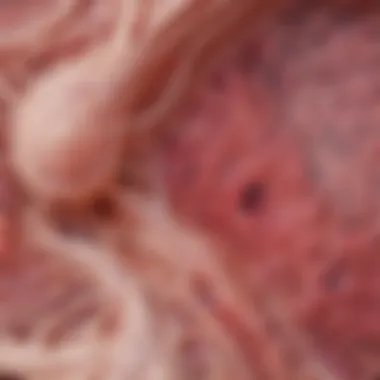

The fatty hilum is a vital anatomical feature located within the lymph node. This region is where the lymphatic vessels enter and exit, facilitating the transport of lymph. It is composed mainly of adipose tissue that supports the node's structure and serves as a reservoir for immune cells.
The presence of fatty tissue can play a role in interpreting imaging studies, as it often indicates healthy lymph nodes. In clinical assessments, the fatty hilum can serve as a distinguishing feature that helps differentiate benign from malignant conditions. A well-defined hilum generally suggests a benign process, while an ill-defined or absent hilum could raise suspicion for malignancy.
Histology of Fatty Hilum in Lymph Nodes
From a histological perspective, the fatty hilum exhibits distinct cellular and structural components. The histology reveals a rich background of adipocytes, which are vital to the metabolic activities of the lymph node.
- Adipose Cells: These cells store energy and release signaling molecules that may modulate immune functions.
- Vascular Structures: Blood vessels within the hilum are prominent, providing necessary nutrients and facilitating immune cell migration.
- Extracellular Matrix: The hilum's integrity is supported by a network of fibers that encases the adipocytes.
Overall, the histological examination of the fatty hilum can yield significant insights into the functional status of lymph nodes and their response during infection or malignancy.
Understanding these elements are crucial for clinicians and researchers alike to ascertain the health of breast tissue and the underlying lymphatic system.
In summary, the anatomical structure of lymph nodes, particularly the components of the fatty hilum, plays a pivotal role in their immune functions and clinical diagnostic relevance.
Imaging Techniques for Evaluating Lymph Nodes
Imaging plays a crucial role in the evaluation of lymph nodes, especially those containing fatty hilum in the breast. These techniques help in assessing not only the size but also the morphology of lymph nodes, which can provide significant clues regarding their health status. Accurate evaluation of lymph nodes aids in differentiating benign conditions from potential malignancy. The choice of imaging technique can influence diagnostic outcomes, thus understanding the various imaging modalities is essential.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is often the first-line method for evaluating lymph nodes in breast tissue. This technique uses sound waves to produce images of the internal structures. Lymph nodes appear as distinct entities on ultrasound, and the presence of a fatty hilum often indicates a benign process.
- Benefits: Ultrasound is non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it safer for patients. It can be performed quickly and provides real-time images. Furthermore, it allows for guided biopsies if abnormalities are detected.
- Considerations: Operator skill can significantly impact the results. Also, the visualization may be limited by factors such as patient body habitus or operator experience.
MRI in Assessing Breast Lymph Nodes
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has become increasingly relevant in the assessment of breast lymph nodes, particularly in complex cases. MRI provides detailed cross-sectional images and enhances the visualization of soft tissue structures.
- Benefits: MRI is particularly effective in characterizing the attributes of lymph nodes. This can help in distinguishing between benign and malignant nodes based on their morphology, enhancement patterns, and surrounding tissues.
- Considerations: MRI has a higher cost and requires longer examination times. Patients with certain implants or claustrophobia may find it challenging. Additionally, the interpretation of MRI images requires significant expertise.
Role of CT Scan in Lymph Node Evaluation
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are less commonly used for evaluating lymph nodes associated with breast conditions but can provide valuable information in specific scenarios. CT is particularly useful when assessing lymph nodes in a more systemic context, such as mapping the lymphatic spread of breast cancer.
- Benefits: CT scans are quick and widely available. They can simultaneously assess other abdominal and thoracic structures, providing a comprehensive view of potential metastases.
- Considerations: The use of contrast media may pose risks for some patients, and exposure to radiation is a significant concern. CT's ability to evaluate lymph nodes is generally less detailed compared to MRI or ultrasound, particularly on a microscopic level.
Ultimately, the choice of imaging technique depends on the clinical context, patient history, and physical examination findings.
By leveraging these imaging modalities, healthcare providers can obtain critical information necessary for effective diagnosis and treatment planning. This comprehensive approach allows for better management of patients presenting with issues related to lymph nodes in the breast.
Clinical Significance of Fatty Hilum in Lymph Nodes
Understanding the clinical significance of fatty hilum in lymph nodes is essential for comprehending breast health. The presence or absence of fatty hilum can indicate various underlying conditions. Its evaluation can assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing the features of lymph nodes with fatty hilum increases the likelihood of precise and effective management of breast disorders.
Benign Conditions Associated with Fatty Hilum
Fatty hilum in lymph nodes is often observed in benign conditions. Conditions like reactive lymphadenitis or lymphoma can lead to the retention of fat within the node. When fatty hilum is present, it usually suggests a node still functioning well. Some benign conditions associated with this feature include:
- Infectious causes: Such as viral infections that provoke a mild response without malignancy.
- Non-specific inflammation: Resulting from local trauma or irritation that doesn’t indicate serious disease.
- Benign tumors: Like lipomas can also maintain innocent fatty hilum structures.
Healthcare providers consider these benign conditions during evaluations. When reviewing imaging or pathology reports, the fatty hilum's presence can indicate that the lymph node is not involved in a malignant process. Knowing these details helps avoid unnecessary invasive procedures.
Malignant Lymph Nodes and Diagnostic Implications
On the other hand, the presence of fatty hilum does not always guarantee benign conditions. Malignant lymph nodes may occasionally exhibit fatty hilum. It's critical to differentiate between benign and malignant processes.
Some malignancies may show altered hilum features while still maintaining fat content. This can confuse diagnosis. Notably, in cases of breast cancer, lymph nodes with fatty hilum need closer examination.
- Cancers that affect lymph nodes: Such as breast cancer can alter the normal architecture of fatty hilum.
- Metastasis evaluation: Understanding the lymphatic involvement can be pivotal for selecting treatment strategies.
End of Clinical Significance
In summary, fatty hilum in lymph nodes plays a crucial role in both benign and malignant conditions. While benign nodes are straightforward, malignant nodes require careful assessment.
"The analysis of fatty hilum not only assists in diagnoses but shapes treatment pathways significantly."
Medical practitioners rely on the presence of fatty hilum in lymph nodes during evaluations to determine the necessary interventions. Overall, a thorough understanding of this topic enhances diagnostic accuracy and improves patient outcomes.


Pathological Conditions Impacting Lymph Nodes
Understanding pathological conditions impacting lymph nodes is vital in the context of breast health. These conditions often serve as indicators of underlying disease processes. The lymphatic system, particularly in the breast, is instrumental in filtering lymph fluid and responding to pathological changes. Recognizing how these conditions manifest can significantly inform diagnosis and treatment strategies, providing insights that help distinguish benign issues from potentially malignant ones.
Lymphadenopathy in Breast Disorders
Lymphadenopathy refers to the enlargement of lymph nodes. In breast disorders, it can indicate various pathological processes, both benign and malignant. This enlargement can arise due to infections, autoimmune diseases, or malignancies, each presenting with differing implications for patient care.
- Benign Causes: Infections, such as mastitis, often lead to localized lymphadenopathy. The nodes may swell as they respond to inflammation. Other benign causes include lymphatic drainage issues following surgical interventions.
- Malignant Causes: Conversely, significant lymph node enlargement can suggest breast cancer metastasis. Cancerous nodes tend to present with a hard consistency and fixed positions, contrasting with the softer, mobile nodes seen in benign conditions. Recognizing these differences is crucial for clinical assessments.
It is also important to consider imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, which can provide clarity on the nature of lymphadenopathy. The presence of fatty hilum within lymph nodes may often indicate a benign condition; however, further evaluation is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Inflammatory Conditions Affecting Lymph Nodes
Inflammatory conditions can profoundly affect lymph nodes in the breast. These conditions trigger an immune response, causing lymph nodes to react in ways that may be difficult to interpret at first glance. The identification of inflammation is crucial for appropriate management.
- Mastitis: This is a common inflammatory condition, especially in lactating women. Mastitis results in swollen and painful lymph nodes, often associated with fever and redness in the breast tissue.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to lymphadenopathy. In these cases, affected nodes may appear enlarged even without direct infection.
Monitoring inflammatory markers and lymph node response can provide essential information about the underlying pathology, guiding therapeutic approaches accordingly.
"Lymph node health serves as a window into broader systemic issues, aiding healthcare professionals in making informed decisions regarding patient care."
In summary, understanding pathological conditions impacting lymph nodes is critical for effective diagnosis and treatment. The context of lymphadenopathy in breast disorders allows for the identification of benign versus malignant processes. Additionally, knowledge of inflammatory conditions provides healthcare providers with insights necessary for managing these patients effectively.
Research Developments in Lymph Node Studies
Exploring lymph nodes with fatty hilum brings to light recent advances in research. It is essential as these findings directly impact clinical practice and diagnosis. With a better understanding of lymph node variability, medical professionals can significantly enhance their approach to patient care and treatment strategies. This reflects the importance of ongoing studies in the realm of lymphatic health, especially concerning breast tissue.
Recent Findings on Fatty Hilum Variability
Recent studies have scrutinized the variability of fatty hilum within lymph nodes. Researchers have discovered that the presence, size, and distribution of fat in the hilum can vary greatly. This variability sometimes correlates with age, body mass index, and even underlying health conditions. Understanding these differences helps in refining diagnostic criteria and improving interpretations of imaging studies.
In particular, some interesting findings show that:
- Fatty hilum can appear larger in patients with certain benign conditions.
- The presence of a fatty hilum may indicate the non-malignant nature of lymph nodes, thus assisting in differentiating between benign and malignant cases.
- Studies have also pointed to genetic and environmental factors influencing fatty hilum development.
"The variability of fatty hilum must be understood in the context of overall health, as it can provide insights into both normal and pathological lymphatic function."
Emerging Technologies in Lymph Node Analysis
Newer technologies are integral to advancing our understanding of lymph nodes, particularly regarding the fatty hilum. Innovations in imaging techniques and histological examination techniques are enhancing the detection and analysis of lymph node characteristics.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Technologies such as 3D ultrasound and high-resolution MRI have opened pathways to visualize lymph node structure with greater clarity. These techniques allow for the assessment of fatty hilum in detail, potentially leading to improved accurate diagnoses.
- Molecular Imaging: This approach highlights specific biological processes within nodes, offering insights beyond standard imaging. It helps in identifying changes that may not be visible through traditional methods.
- Data Analysis Software: Utilizing artificial intelligence enables more profound data insights from imaging studies. AI algorithms can identify patterns and oddities in the structure of fatty hilum, thereby assisting in diagnostic efforts.
By integrating these technologies, researchers and clinicians can approach lymph node analysis with better tools. The future promises even more refinements, potentially benefiting patient outcomes in breast health and beyond.
Comparative Anatomy of Lymph Nodes Across Species
The comparative anatomy of lymph nodes across species is significant for understanding the evolution and functionality of the lymphatic system. It enables researchers to identify common structures and variations in lymph nodes among mammals, highlighting how these differences can influence the immune response and disease susceptibility. Insights gained from such comparisons can also inform medical research and veterinary practices.
Lymphatic Structures in Mammals
Mammals exhibit a range of lymphatic structures that support the immune system. These structures perform key roles in the collection and transport of lymph fluid. Generally, lymph nodes are strategically located near major internal organs or lymphatic vessels. This positioning facilitates the filtering of lymph and the activation of immune cells against pathogens.
- Cortex and Medulla: In most mammals, lymph nodes are organized into compartments. The cortex contains lymphatic follicles where B cells proliferate, while the medulla houses medullary cords and sinuses involved in the processing of immune responses.
- Hilum: The hilum is a central region where blood vessels enter and exit the lymph node. The presence of fatty hilum varies among species.
- Sinuses: Lymphatic sinuses are present in the lymph nodes, facilitating the flow of lymph and allowing for interaction with immune cells.
Different mammalian species have unique adaptations in their lymphatic structures. For instance, rodents often possess larger lymph nodes relative to their body size, which can be linked to their active immune responses.
Species-Specific Variations in Fatty Hilum
The fatty hilum serves as a notable feature in lymph nodes and shows variation across species.
- Role in Imaging: In imaging studies, the appearance of the fatty hilum can assist in differentiating between benign and malignant lymph nodes. For example, in humans, a well-defined fatty hilum often indicates a benign node, while its absence may raise suspicion for malignancy.
- Comparative Studies: Studies on animals such as dogs and cats reveal that their fatty hilum can appear more prominent than in some other mammals, suggesting differences in metabolic requirements for the lymphatic system.
- Functional Implications: The fatty hilum's presence may imply differences in the lymphatic load and the need for fat storage or energy reserves within the lymph nodes. For instance, species with higher fat reserves may exhibit differently shaped or sized hila compared to those that are leaner.
These comparative aspects help in understanding not only lymph node structure but also the broader implications for health, disease, and anatomical research.


"Understanding the variations in lymph nodes can lead to better diagnostic practices and tailored treatments based on species-specific physiology."
Overall, comparative anatomy sheds light on the versatile nature of the lymphatic system across mammals. Areas of future research may include the functional consequences of these differences as well as their relevance in evolutionary biology.
The Role of Fatty Hilum in Breast Cancer Prognosis
The role of the fatty hilum in lymph nodes, specifically in the context of breast cancer prognosis, cannot be understated. The presence and characteristics of fatty hilum in lymph nodes can provide vital insights into disease progression and patient outcomes. Understanding these implications is critical for both diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in breast cancer management.
Fatty Hilum as a Biomarker
Fatty hilum in lymph nodes is recognized as an important biomarker. This specific area within the lymph node is composed of adipose tissue that often appears in healthy lymph nodes. In cases of malignancy, alterations to the fatty hilum can occur, which may impact prognosis.
When the fatty hilum is intact and appears prominent on imaging studies, it suggests that the lymph node is likely benign. The intact fatty hilum acts as a reassuring sign, indicating that the node has not undergone significant pathological changes. Conversely, if the fatty hilum is obscured or transformed due to disease processes, it may indicate infiltration by cancerous cells, thus raising concerns about potential metastasis.
Several studies point to the correlation between the presence of a clear fatty hilum and better outcomes in breast cancer patients. Monitoring changes to this biomarker can be influential in identifying patients at higher risk of advanced disease. Recognizing these patterns can enhance the accuracy of clinical evaluations, leading to more effective treatment planning.
Impact on Treatment Decisions
The visibility and condition of the fatty hilum influence treatment choices considerably. For clinicians, the presence of a fatty hilum can steer the direction of surgical or non-surgical interventions. If imaging reveals a clear fatty hilum, healthcare providers may lean towards less aggressive treatment options. This is because such findings typically correlate with lower likelihoods of malignancy.
In cases where the fatty hilum is absent or replaced by pathological tissue, more aggressive management could be required. Such patients might need surgical resection or adjuvant therapies, including chemotherapy or radiation, to ensure comprehensive disease control.
- Surgical Strategies:
- Monitoring:
- Minimal intervention may be taken for lymph nodes with preserved fatty hilum.
- Extensive surgical approaches are favored if the hilum is affected.
- Regular imaging may be preferred for patients with benign presentations.
- For nodes showing alterations, closer monitoring or immediate intervention might be warranted.
Ultimately, understanding the role of fatty hilum enhances clinical decision-making. Providers can tailor treatment plans based on this critical marker, ensuring patients receive appropriate care rooted in their specific lymph node status.
"The assessment of fatty hilum should be an integral part of pre-treatment evaluation in breast cancer. Its role as a biomarker cannot be overlooked."
In summary, the study of the fatty hilum in breast lymph nodes serves profound implications for breast cancer prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment. As research evolves, it may further refine our approach to managing lymphatic health and cancer care.
Future Directions in Research
Research in lymph nodes with fatty hilum holds significant promise for advancing our understanding of breast health. This segment evaluates the evolving landscape of this research field, highlighting critical elements such as potential therapeutic advancements and the necessity for longitudinal studies.
Potential for Novel Therapeutics
The exploration of lymph nodes with fatty hilum may unveil innovative therapeutic pathways. Recent studies suggest that the characteristics of the fatty hilum could influence immune responses and tumor behavior, leading to the hypothesis that manipulating these lymphatic structures might enhance therapeutic efficacy.
For instance, researchers are investigating if targeting the fatty hilum through specific drugs can aid in the management of lymphatic diseases or breast cancer. This could potentially lead to an improved understanding of how fat tissue within lymph nodes interacts with surrounding cells, influencing overall immune function and tumor progression.
"Targeting the lymphatic system may provide a new avenue for therapeutic intervention, shifting from traditional treatments to more tailored approaches."
In this context, ongoing collaboration among immunologists, oncologists, and researchers in lymphatic biology will be crucial. Work must center on identifying molecular targets within the fatty hilum, optimizing drug delivery systems, and assessing the impact of such treatments in clinical settings.
Longitudinal Studies on Lymphatic Health
Longitudinal studies are vital for understanding the dynamic changes in lymphatic health. Tracking alterations in the fatty hilum over time can provide insights into underlying pathologies, both benign and malignant. Conducting such studies involves regular monitoring of patients through imaging techniques and biopsies, ensuring detailed observations of the lymphatic response.
One focal point for these studies could be the association between fatty hilum characteristics and the progression of breast cancer. Observing trends over years could reveal patterns that inform prognosis and treatment strategies.
Furthermore, longitudinal studies offer the advantage of identifying risk factors associated with lymph node changes. This can lead to early interventions for at-risk populations and can inform public health strategies.
Epilogue
The importance of understanding lymph nodes with fatty hilum in the breast is emphasized throughout this article. This topic reveals essential aspects of both anatomy and pathology, guiding healthcare providers in their diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. The interplay between lymphatic health and breast disorders serves as a fundamental aspect in patient care, paving the way for improved outcomes.
Summary of Key Concepts
In review, lymph nodes with a fatty hilum indicate specific physiological and structural properties that carry significant implications. This article highlights the following key concepts:
- Anatomy and Function: Lymph nodes play a crucial role in filtering lymphatic fluid and housing immune cells. The presence of fatty hilum within these nodes can signify benign conditions.
- Diagnostic Relevance: Imaging techniques, including ultrasound and MRI, allow for better visualization and assessment of lymph nodes, facilitating diagnosis while distinguishing between benign and malignant conditions.
- Clinical Implications: Recognizing the characteristics associated with fatty hilum aids in prognostic evaluations, influencing treatment decisions based on node status.
Researchers and clinicians should stay updated on the advancements and research findings surrounding lymphatic health in the breast to better inform their practice and improve patient care.
Implications for Healthcare Providers
For healthcare providers, understanding the nuances of lymph nodes with fatty hilum goes beyond mere anatomy; it involves a thorough comprehension of its clinical significance. Some important implications are listed below:
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Familiarity with how fatty hilum appears on imaging can help differentiate between benign and malignant lymph nodes.
- Tailored Treatment Strategies: Knowledge of lymphatic health informs decisions regarding treatments, therapies, and patient management.
- Ongoing Research Participation: Engaging with current studies in lymphatic health allows providers to apply the most recent findings to their clinical practice.



