Lisinopril and Psoriasis: Exploring Their Link
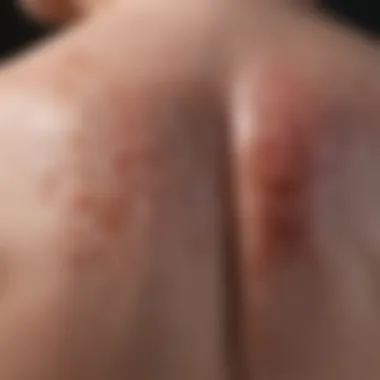

Intro
The interaction between medications and various health conditions is a crucial area of research in modern medicine. One intriguing connection is between lisinopril, a commonly prescribed antihypertensive medication, and psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition. As prevalence of psoriasis rises, understanding its triggers, including potential triggers from medications like lisinopril, is essential for effective patient care.
Lisinopril is widely recognized for its role in managing high blood pressure and treating heart failure. However, its pharmacological effects could inadvertently influence skin health in some patients. This article delves into studies and literature to explore whether lisinopril may exacerbate psoriasis symptoms or emerge as a contributing factor to the condition's onset. Through a systematic review, we aim to clarify the implications for patients using lisinopril and to assist healthcare professionals in refining treatment plans.
By examining the existing body of research, we aim to develop a clearer picture of this connection. In the following sections, we will articulate key findings and provide an overview of the methodologies employed in these investigations.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Current literature presents mixed results regarding the relationship between lisinopril and psoriasis. Some studies indicate that certain antihypertensive agents, including lisinopril, may trigger or worsen symptoms in susceptible individuals. However, others posit that lisinopril could help manage inflammatory processes associated with chronic skin conditions. This contradiction suggests a nuanced interplay between medication and the body's physiological responses.
- Possible exacerbation: Several cases documented in clinical settings have observed worsening psoriasis symptoms in individuals starting lisinopril.
- Lack of conclusive evidence: Despite anecdotal reports, well-controlled studies are sparse, creating a gap in our understanding.
- Potential benefits: Some researchers encourage further investigation into lisinopril's anti-inflammatory properties, which could beneficial in specific contexts.
Relevance to Current Scientific Discussions
The ongoing debate around the safety profile of antihypertensive medications, particularly lisinopril, is timely. With psoriasis affecting millions worldwide, understanding potential risk factors associated with common medications could reshape treatment options.
Discussions among healthcare providers have increasingly highlighted the importance of personalized medicine. Identifying patients at risk of developing psoriasis symptoms when prescribed lisinopril could facilitate more tailored therapeutic approaches.
Methodology
Research Design and Approach
A systematic review approach was adopted to collate and evaluate existing studies. This method allows for a comprehensive assessment of diverse research findings and enhances the reliability of conclusions drawn.
The selection criteria focused on peer-reviewed articles that explored the relationship between psoriasis and lisinopril. Emphasis was placed on studies that included both observational and clinical trial data.
Data Collection and Analysis Techniques
Data was retrieved from various medical databases, including PubMed and Web of Science. The analysis involved identifying prevalence rates, patient experiences, and pharmacological impacts observed in published literature.
- Literature search: Selected articles were filtered based on relevance and contribution to the identified research question.
- Data synthesis: Extracted information was categorized into themes, enabling detailed comparisons across studies.
This systematic exploration lays the groundwork for understanding the nuances of this connection. Further research is warranted to validate these findings and elucidate the mechanisms at play.
Preface to Lisinopril and Psoriasis
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the relationship between medication and skin conditions, particularly autoimmune diseases like psoriasis. This section introduces lisinopril, a widely prescribed antihypertensive drug, alongside psoriasis, which is a chronic skin disorder affexted by immune response. Understanding their connection is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Lisinopril is commonly used to manage high blood pressure and heart failure. It works by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure. However, the long-term use of any medication can lead to various side effects, including potential implications for skin health. This article explores whether lisinopril may influence the onset or worsening of psoriasis symptoms. The findings can aid both patients who take lisinopril and healthcare providers responsible for crafting effective treatment regimens.
On the other side, psoriasis is characterized by patches of inflamed skin, often leading to significant discomfort and a decreased quality of life. It is largely driven by dysfunctional immune responses, which result in excessive skin cell production. Exploring the interaction between lisinopril and psoriasis is vital because if lisinopril exacerbates psoriasis symptoms, it necessitates discussions on alternative treatments for managing hypertension without compromising skin health.
Thus, this section sets the groundwork for a deeper exploration into the mechanisms of action, patient experiences, and clinical implications relating to the association between lisinopril and psoriasis. Analyzing how these two elements may interlink could provide insights that establish better treatment protocols for individuals affected by both hypertension and psoriasis.
Defining Lisinopril
Lisinopril is classified under the category of ACE inhibitors. It is primarily prescribed to treat hypertension and heart failure. By blocking the action of angiotensin II, lisinopril helps relax blood vessels, which in turn lowers blood pressure. Patients often appreciate its effectiveness and relatively mild side effects compared to other classes of antihypertensive medications.
Moreover, lisinopril is sometimes utilized in treating diabetic kidney disease due to its protective effect on renal function. Its broad application in clinics makes it an essential component in managing cardiovascular health. However, understanding its long-term implications on skin conditions, such as psoriasis, is just as critical.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin. This disorder can manifest in various forms, but the most common type is plaque psoriasis, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. The condition can vary significantly in severity and can affect any body part, including the scalp, elbows, and knees.
The pathophysiology of psoriasis involves immune system dysregulation, leading to an inflammatory response that accelerates skin cell turnover. This fast-paced lifecycle of skin cells results in the visible symptoms of psoriasis. Factors such as stress, trauma, and certain medications can trigger flare-ups, emphasizing the need to understand the potential implications of various treatments, including lisinopril.
Changes in skin conditions when taking medications like lisinopril warrant careful consideration for those managing both psoriasis and hypertension. Further exploration through clinical studies and patient observations may provide clarity in connecting lisinopril to any changes in psoriasis symptoms.

Mechanism of Action for Lisinopril
Lisinopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, and understanding its mechanism is vital in analyzing its potential link to psoriasis. The importance of this topic lies in its pharmacological properties, which can influence various systems in the body, including the immune system, blood pressure regulation, and inflammation pathways.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition
ACE inhibitors like lisinopril work by blocking the action of the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which is responsible for converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a peptide that narrows blood vessels and raises blood pressure. By inhibiting this enzyme, lisinopril allows for the dilation of blood vessels, leading to lower blood pressure and reduced strain on the heart.
Key Points:
- Lower blood pressure can lead to reduced cardiac workload.
- This mechanism may also influence levels of cytokines, which can affect inflammatory conditions.
- ACE inhibitors can promote vasodilation, impacting various tissues in the body, including the skin.
The inhibition of ACE and subsequent reduction in angiotensin II levels might play an indirect role in inflammatory processes affecting conditions like psoriasis.
Effects on Blood Pressure and Vascular Health
The effect of lisinopril on blood pressure and vascular health cannot be overlooked. It not only contributes to improved overall cardiovascular function but may also have downstream effects that influence skin conditions such as psoriasis.
Considerations include:
- Vascular Health: Improved blood flow and oxygen delivery to the skin may impact skin healing and inflammation.
- Blood Pressure Management: Effective management of hypertension minimizes cardiovascular diseases that can complicate chronic conditions.
- Potential Side Effects: Some patients may experience skin-related side effects, which could necessitate close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
By understanding the mechanism of action for lisinopril, we can better interpret its significance in psoriasis management and its potential negative or positive effects on the condition.
The dual nature of lisinopril's action in manipulating both blood pressure and inflammatory processes is worthy of detailed exploration when discussing its association with psoriasis.
Psoriasis: Pathophysiology and Triggers
Understanding the pathophysiology and triggers of psoriasis is crucial in the context of this article. Psoriasis is a complex autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell proliferation, leading to the formation of plaques. Identifying the underlying mechanisms that contribute to this disease can illuminate how certain medications, like lisinopril, may impact its symptoms. Additionally, recognizing the various triggers that can provoke flare-ups allows for better management strategies tailored to individual patients.
Immunological Factors in Psoriasis
Psoriasis is heavily influenced by the immune system. Specifically, T cells play a vital role in its development. When activated, these cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines, which stimulate the proliferation of skin cells. This excessive growth is a hallmark of psoriasis. The involvement of cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-17 supports a chronic inflammatory state.
Research indicates that immunological dysregulation, often precipitated by environmental triggers, can lead to a heightened immune response. This response does not only affect the skin but can have systemic implications as well. Thus, understanding these factors is essential, especially when evaluating how treatments like lisinopril could potentially affect psoriasis patients.
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers
Several environmental and lifestyle factors exacerbate psoriasis. These include stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and skin injuries. Each trigger can instigate an immune response that exacerbates the inflammatory process.
Common environmental triggers include:
- Infections: Such as streptococcal infections.
- Weather Changes: Cold and dry weather can worsen psoriasis.
- Medications: Certain drugs can induce or aggravate psoriasis symptoms.
In managing psoriasis, addressing these triggers can lead to significant improvement. It is important for patients to monitor their lifestyle and environmental factors, as understanding their specific triggers can be beneficial in managing the condition. Healthcare providers can aid in this process by recommending changes and introducing appropriate therapies.
Association Between Lisinopril and Psoriasis
Understanding the connection between lisinopril and psoriasis is essential for several reasons. Lisinopril is a widely prescribed medication for hypertension and heart failure, making it a common treatment choice for many patients. As psoriasis affects a considerable segment of the population, particularly those with cardiovascular issues, the interplay between these two health concerns must be examined.
By closely evaluating the potential associations, healthcare providers can offer more tailored treatment plans that minimize risks while maximizing benefits. Given the complexity of both conditions, this focus brings to light the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in patient care.
Research into this association can provide critical insights that not only influence clinical outcomes but may also guide patients in managing their health more proactively. This reinforces the importance of continuous monitoring and reporting of any psoriasis symptoms in patients taking lisinopril.
Review of Clinical Studies
Clinical studies provide much of the evidence required to understand any potential link between lisinopril and psoriasis. A review of existing literature reveals varied findings. Some studies suggest that individuals taking lisinopril experience different skin reactions compared to those on other antihypertensives, while others show no significant correlation.
For instance, one analysis published in the Journal of Dermatology found that patients using lisinopril reported increased psoriasis symptoms in a small subset of cases. The mechanisms suggested include the modulation of immune response and changes in skin microcirculation caused by the medication. Other studies indicated that lisinopril does not consistently provoke psoriasis flares, implying that other factors may play a more critical role in exacerbating the condition.
Case Reports and Observational Data
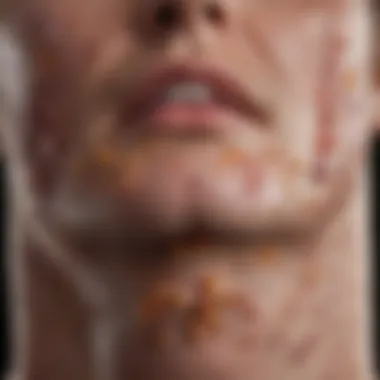

Beyond clinical trials, case reports and observational data serve to highlight individual experiences that can inform the broader understanding of lisinopril's effects on psoriasis. Anecdotal evidence from patients showcases a range of responses to lisinopril, with some reporting an improvement in their psoriasis symptoms, while others note worsening.
"After starting lisinopril, my blood pressure improved, but I noticed my psoriasis became more inflamed. It was frustrating to manage both issues together."
This variability underscores the need for careful documentation and case collection regarding patients' experiences when using lisinopril. Healthcare providers must consider these reports seriously when assessing treatment efficacy and safety. Continuous engagement with patients will enable clinicians to gather valuable data, which may ultimately reveal patterns or risk factors associated with psoriasis worsening in the context of lisinopril use.
Potential Mechanisms Linking Lisinopril to Psoriasis
Understanding how lisinopril may relate to psoriasis requires examining various underlying mechanisms. This topic is critical for both clinical practitioners and researchers. By identifying potential pathways involved, we can better evaluate the implications for patients on lisinopril. The analysis will focus on two specific areas: the role of angiotensin II in inflammation and the impact on immune response. Both of these elements can significantly influence the chronic nature of psoriasis symptoms.
Role of Angiotensin in Inflammation
Angiotensin II is a potent vasoactive peptide that plays a key role in the body’s response to stress. It is formed from angiotensin I through the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme, which is what lisinopril inhibits. The actions of angiotensin II are many and include the promotion of inflammatory responses. In the context of psoriasis, this substance can exacerbate inflammation in the skin.
- Inflammation Process: Angiotensin II contributes to the recruitment of immune cells to inflamed skin areas. This recruitment amplifies the inflammatory cycle typical in psoriasis.
- Cytokine Production: The molecule is associated with the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are critical in psoriasis development.
- Effects on Vascular Health: Angiotensin II influences vascular permeability. This strains the skin’s integrity and may facilitate psoriasis flare-ups.
In summation, the role of angiotensin II suggests a possible link. If lisinopril lowers angiotensin II levels effectively, it might contribute to reduced inflammation in psoriasis patients.
Impact on Immune Response
The immune system intricately contributes to psoriasis pathology, being primarily an autoimmune condition. The effect of lisinopril on immune response offers another perspective on its relationship with psoriasis.
- Modulation of Immune Cells: Lisinopril may alter the function and proliferation of T-cells, a type of white blood cell activated in psoriasis outbreaks.
- Reduction of Systemic Inflammation: By promoting lower blood pressure and altering the local environment, lisinopril might indirectly mitigate systemic inflammation capabilities.
- Connection to Autoimmunity: Effective control of hypertension has potential benefits on general immune health. This may provide an indirect positive impact on patients with autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis.
Through this systematic approach, we can make strides in clarifying the potential implications of lisinopril use for psoriasis sufferers.
Perspectives from Healthcare Professionals
Understanding the viewpoints of healthcare professionals is crucial in addressing the connection between lisinopril and psoriasis. This perspective offers insights from those who manage patients affected by both hypertension and skin conditions. By examining their experiences, we can uncover potential links that may influence treatment strategies and patient outcomes. Input from these professionals can highlight not only clinical observations but also best practices in managing patients taking lisinopril as part of their hypertension treatment regimen.
Viewpoints from Dermatologists
Dermatologists, who specialize in skin conditions, often navigate complex cases of psoriasis. Their observations regarding changes in psoriasis symptoms in patients taking lisinopril can reveal important trends. Some dermatologists may report that certain patients experience exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms after starting this medication, while others may not notice significant changes. This variability underscores the need for careful monitoring of patients and individualized treatment plans.
Dermatologists are also aware of the pharmacological mechanisms at play. They may explore how lisinopril's effects on blood pressure and vascular health could indirectly influence skin health, particularly in psoriasis, which is known to be impacted by vascular factors. Their clinical expertise can help bridge the gap between general medical understanding of lisinopril and its specific implications for dermatological health.
Input from Cardiologists
Cardiologists provide a complementary perspective regarding lisinopril usage among patients who have hypertension. As lisinopril is frequently prescribed for managing high blood pressure, cardiologists balance its benefits with any potential side effects that might arise, including those related to psoriasis. Some cardiologists might note that appropriate management of hypertension is vital for overall cardiovascular health, which can have cascading effects on other conditions, including skin disorders.
Furthermore, cardiologists frequently emphasize the necessity of a multi-disciplinary approach in treating patients. When patients exhibit skin issues while on lisinopril, they are likely to consult with dermatologists. Such collaboration ensures a holistic view of the patient, considering the interplay between hypertension management and dermatological conditions.
Through their combined insights, dermatologists and cardiologists enhance our understanding of the relationship between lisinopril and psoriasis. Their collective experiences can foster a more informed dialogue about treatment protocols, informing future studies and clinical practices. This holistic approach is essential in creating tailored treatment plans, ultimately improving patient health outcomes.
Patient Experiences and Anecdotal Evidence
In examining the relationship between lisinopril and psoriasis, patient experiences and anecdotal evidence provide crucial insights. While clinical studies offer a scientific framework, patients' perspectives reveal the realities of living with psoriasis while on this medication. Gathering qualitative data from patients can highlight both positive and negative experiences, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of how lisinopril may impact psoriasis symptoms.
Each patient’s experience can differ significantly. For some, the onset of psoriasis coincides with the initiation of lisinopril, while others may report no correlation at all. These personal stories can shed light on the complexities of this relationship. Understanding these anecdotal scenarios is vital both for clinicians and researchers, as they inform the real-world implications of using lisinopril in patients susceptible to skin conditions.
Surveys and Patient Feedback
Surveys can serve as a valuable tool in collecting patient feedback regarding their experiences with lisinopril and psoriasis. By asking targeted questions, healthcare providers can gauge the prevalence of psoriasis symptoms among those taking lisinopril. Information gathered may include the duration of treatment, severity of psoriasis symptoms, and any additional factors such as family history or lifestyle habits.
Through patient feedback, specific trends may emerge. For instance, certain demographics might report intensified symptoms after starting lisinopril. Unlike randomized controlled trials, surveys capture diverse voices, potentially uncovering underreported effects caused by the medication.
Furthermore, the feedback can assist in shaping guidelines for managing psoriasis in patients who are prescribed lisinopril.
Case Studies Documenting Outcomes
Case studies present another layer of detail in understanding the relationship between lisinopril and psoriasis. These in-depth accounts allow for examination of individual cases, providing context that broad clinical studies may overlook. A single case study may document a patient's psoriasis progression, detailing factors such as medication history, treatment responses, and lifestyle influences.


For instance, a case study might illustrate a patient who initially had well-controlled psoriasis that worsened after the introduction of lisinopril. Documentation of such experiences can be crucial for professionals trying to tailor treatment plans.
In addition, it can serve to raise awareness about potential risks among patients taking lisinopril. By sharing these detailed narratives, healthcare providers can gain insights into how to manage and anticipate treatment outcomes more effectively.
"Anecdotal evidence might not carry the same weight as clinical trials, yet it provides essential context and expresses the nuances of patient experiences which numbers alone cannot convey."
Comparative Analysis with Other Antihypertensives
This section seeks to underscore the significance of understanding how lisinopril compares to other antihypertensive medications concerning its impact on psoriasis. Analyzing this aspect is essential for several reasons. Firstly, patients may be prescribed different classes of antihypertensives based on individual health profiles. Therefore, comprehending how each class interacts with autoimmune conditions like psoriasis becomes imperative. Secondly, the pharmacological properties of these medications may lead to variable effects on skin health, which directly influences treatment choices. Lastly, clinical awareness regarding these distinctions can aid healthcare providers in creating holistic treatment strategies that effectively consider both blood pressure control and skin manifestation management.
Different Classes of Antihypertensives
Antihypertensives are categorized into various classes, each with distinct mechanisms of action, side effects, and interactions with immune conditions. Here are some of the main classes:
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors: These, like lisinopril, block the formation of angiotensin II, helping to lower blood pressure and may also impact inflammatory processes.
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Medications such as losartan fall under this category. They effectively dampen the action of angiotensin II without affecting its production. This distinction could have implications for psoriasis.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Nifedipine and amlodipine are examples. They work by inhibiting calcium influx in vascular smooth muscle, leading to vasodilation. Their influence on immune function may not be as pronounced as ACE inhibitors.
- Beta-Blockers: Drugs like atenolol reduce heart rate and myocardial contractility but may have adverse dermatological side effects, which must be evaluated in psoriasis patients.
- Diuretics: Such as hydrochlorothiazide, primarily promote fluid loss and may have various side effects unrelated to the immune system directly.
Understanding these groups’ basic pharmacology can guide clinicians when faced with psoriasis or other immune-related skin conditions in patients requiring blood pressure management.
Psoriasis Incidence Among Different Medications
Emerging literature indicates that the incidence of psoriasis varies significantly among different classes of antihypertensives. Research shows that:
- ACE Inhibitors: Some evidence suggests that they may have a beneficial effect on some skin conditions, including psoriasis. However, this relationship demands further validation.
- ARBs: Studies indicate that they may present a lower risk of psoriasis exacerbation compared to ACE inhibitors.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: There is less direct evidence linking calcium channel blockers to psoriasis, though individual reactions can vary.
- Beta-Blockers: These have been noted in numerous reports to potentially induce or worsen psoriasis symptoms due to their effects on immune response.
- Diuretics: Generally have a neutral effect on psoriasis status, although side effects like electrolyte imbalances can indirectly impact patient health and treatment.
Understanding these pharmacological distinctions helps tailor treatment approaches for individuals with autoimmunity and hypertension, ensuring comprehensive care.
Clinical Implications and Management Strategies
The intersection of lisinopril and psoriasis raises significant clinical implications. Understanding how lisinopril might impact psoriasis can direct better management strategies for patients with hypertension who also suffer from this skin condition. The integration of this knowledge into clinical practice is essential, as it informs healthcare professionals about possible dermatological effects of the medication. There is a clear need for a dual-focus approach, assessing not only blood pressure but also skin health during treatment with lisinopril. Incorporating this perspective can lead to improved patient outcomes and avoidance of potential medication complications.
Evaluating Risks and Benefits of Lisinopril
Evaluating the risks and benefits of treating hypertension with lisinopril in patients with psoriasis is crucial. Lisinopril is known for its effectiveness in managing high blood pressure and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. However, its connection to psoriasis requires nuanced consideration.
- Risks: Some studies suggest that angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors may be linked to the exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms. The impact of angiotensin II on inflammation may play a crucial role here. Therefore, clinicians must weigh the risk of worsening skin condition against the importance of controlling blood pressure.
- Benefits: On the other hand, the medication also has anti-inflammatory properties that might benefit skin conditions indirectly by improving overall cardiovascular health. In this way, lisinopril may not only help in managing hypertension but also contribute to broader health benefits that could slightly alleviate psoriasis symptoms.
Finding this balance necessitates close monitoring of patients and readiness to adjust treatment plans where needed, ensuring that both hypertension and respiratory health are optimally managed.
Tailoring Treatment Plans for Psoriasis Patients
Tailoring treatment plans for psoriasis patients who are on lisinopril necessitates a holistic view of patient health. Several considerations inform this process:
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Involving both dermatologists and cardiologists can help create cohesive treatment plans. This ensures that all aspects of patient health are assessed and managed.
- Individualized Approach: Every patient's psoriasis can present differently. Factors like the severity of the condition, history of medication response, and overall health should guide the treatment decisions.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous assessment of both skin condition and blood pressure is vital. This approach allows for timely adjustments in medication type or dosage, minimizing adverse effects.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about the potential link between lisinopril and psoriasis symptoms is critical. This knowledge equips patients to report any changes, further aiding in prompt intervention.
- Exploring Alternatives: In cases of serious exacerbation of psoriasis, healthcare providers may explore other antihypertensive options with fewer reports of worsening psoriasis.
Ultimately, creating a tailored treatment strategy improves patient care, demonstrating an effective application of medical knowledge that respects both dermatological and cardiovascular health.
The End and Future Directions
The conclusion of this article emphasizes the critical intersection between lisinopril and psoriasis. As medical professionals and researchers dissect this relationship, it becomes clear that understanding how this common antihypertensive may influence the manifestation of psoriasis is vital. The findings highlight the need to consider patient individualities and the complexities of their conditions when prescribing medications like lisinopril.
Lisinopril, while effective in managing hypertension, may have unintended consequences on skin health. This necessitates elevated awareness among healthcare providers concerning potential dermatological side effects. The exploration within this analysis serves not only as an informative resource but also a beacon for future investigations. It identifies gaps in the current knowledge base regarding lisinopril's role in psoriasis, strengthening the foundation for continued scholarly dialogue.
Summary of Findings
The investigation into the relationship between lisinopril and psoriasis presents an intriguing amalgamation of pharmacology and dermatology. Key findings from the reviewed literature and case studies suggest a multifaceted impact of lisinopril on psoriasis symptoms. Several studies indicate that the drug may exacerbate psoriasis in some patients due to its effects on immune modulation and inflammation. It is prudent to note that while some patients report no adverse effects, others experience a worsening of their condition.
- Lisinopril's mechanism involves angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition, which plays a role in inflammatory pathways.
- Observational data from patients highlight differing responses, reinforcing the need for personalized treatment approaches.
Additionally, the extrapolated data indicate that effects might vary significantly across individuals, necessitating a cautious interpretation of findings and considerations in clinical settings.
"As the understanding of psoriasis evolves, so too must our approach to prescribing medications like lisinopril"
Recommendations for Further Research
Given the preliminary discoveries outlined in this article, further research is essential to comprehensively understand the connection between lisinopril and psoriasis. Future studies should consider the following recommendations:
- Longitudinal Studies: Conducting long-term studies to assess the chronic implications of lisinopril use on psoriasis patients could yield clearer insights.
- Controlled Trials: Implementing controlled clinical trials specifically targeting the psoriasis population would help distinguish effects more definitively.
- Mechanistic Exploration: Investigating the biochemical pathways influenced by lisinopril could elucidate its role in exacerbating or alleviating psoriasis symptoms.
- Patient Demographics: Evaluating how demographics influence response to lisinopril may assist in identifying at-risk patients, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans.



